Understanding the Difference Between Formative and Summative Assessment

Introduction to Formative and Summative Assessment
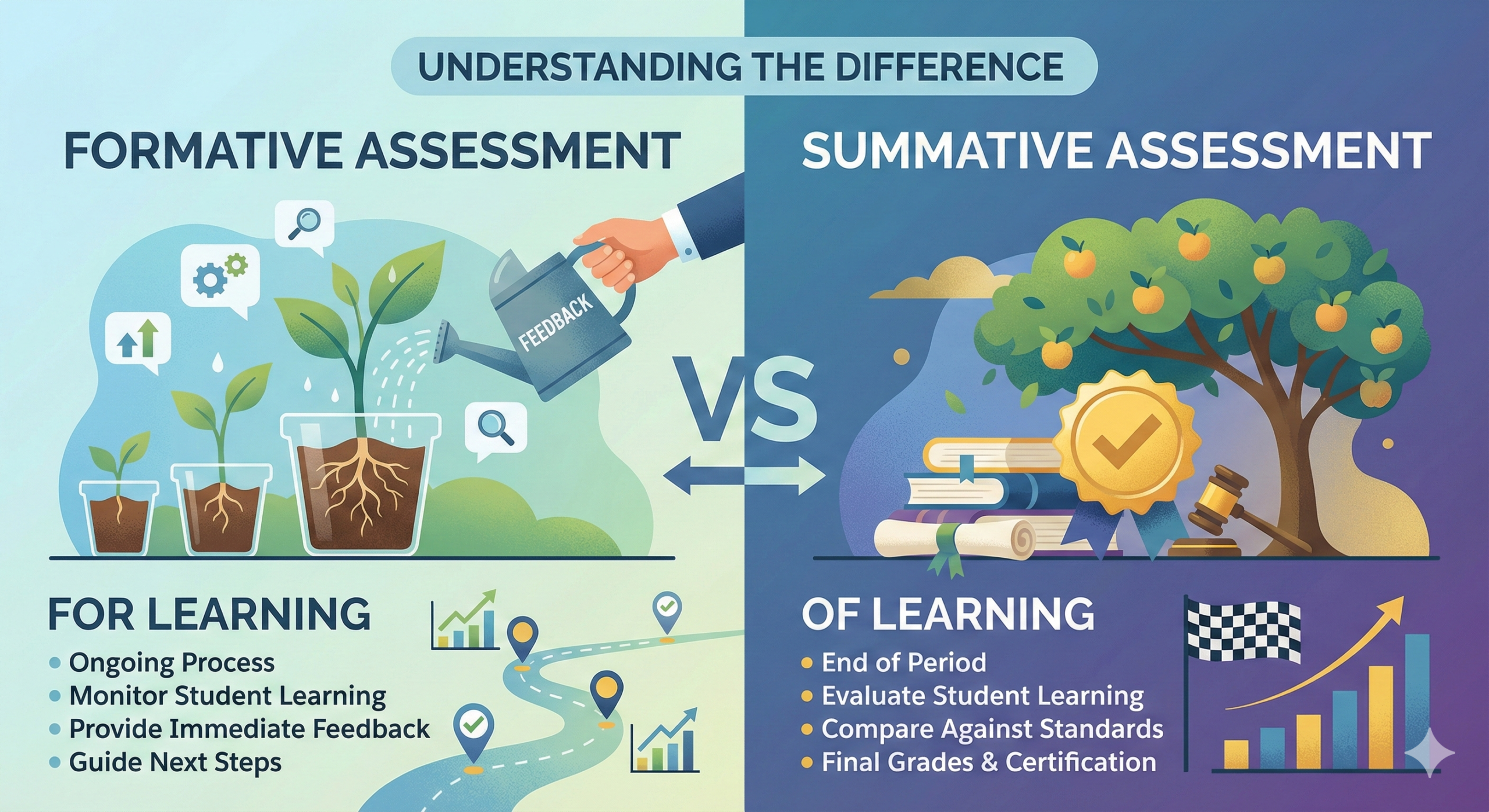
Formative assessment and summative assessment are two fundamental evaluation methods in education, each serving distinct purposes in measuring learners’ understanding and skill acquisition. These concepts are frequently employed when assessing the extent to which students have grasped learning objectives. The conceptual framework underlying these evaluation methods shares notable similarities with design verification and design validation approaches in regulated industries such as medical devices and pharmaceuticals. When these concepts prove difficult to comprehend, recalling the familiar distinction between quizzes (given during a course) and final examinations (given at course completion) can clarify the fundamental differences.
Formative assessment and summative assessment are two fundamental evaluation methods in education, each serving distinct purposes in measuring learner…
Formative Assessment: Evaluation During the Learning Process
Formative assessment is an evaluation method conducted during the learning process itself. A typical example would be a quiz administered after one week of instruction. The results of such formative assessments provide learners with concrete feedback regarding their current level of understanding, identifying areas of strength and those requiring further attention. Simultaneously, educators can evaluate student comprehension and adjust instructional content and teaching methods accordingly to optimize learning outcomes. This iterative process of assessment and adjustment mirrors the concept of “design verification” in regulated product development, where checks and tests confirm that design specifications are correctly implemented during development.
Formative assessment takes various forms in modern educational settings, including classroom discussions, think-pair-share activities, concept mapping exercises, low-stakes quizzes, peer review, and homework assignments. These methods allow educators to gather real-time data on student progress and address misconceptions or knowledge gaps immediately, creating opportunities for timely remediation and enrichment.
Summative Assessment: Evaluation at the End of the Learning Period
In contrast, summative assessment is conducted at the conclusion of a defined learning period. The final examination represents the quintessential example of summative assessment, wherein learners are comprehensively evaluated on their understanding of course content accumulated over a semester or academic year. This approach corresponds to the concept of “design validation” in product development, wherein the entire product is verified to meet its intended use requirements and user needs under actual operating conditions.
Summative assessment typically takes the form of final exams, standardized tests, comprehensive projects, or portfolios that demonstrate achievement of course objectives. These assessments produce a definitive evaluation indicating whether learners have successfully met established learning standards and are prepared to progress to subsequent levels of study or application.
Comparative Overview of Formative and Summative Assessment
| Characteristic | Formative Assessment | Summative Assessment |
| Timing | Conducted during the learning process | Conducted at the end of the learning period |
| Purpose | Monitor progress and guide instruction | Determine whether learning objectives have been achieved |
| Frequency | Frequent and ongoing | Single or limited occurrences |
| Feedback Type | Immediate and actionable | Evaluative and conclusive |
| Use of Results | Modify teaching strategies and content; provide remediation | Assign grades; determine progression; evaluate program effectiveness |
| Conceptual Parallel | Design Verification | Design Validation |
| Stakeholder Focus | Educators and learners | Educators, learners, administrators, and external stakeholders |
Distinct Functions and Complementary Roles
Each evaluation method fulfills distinct yet complementary functions within educational systems. Formative assessment, parallel to design verification, is implemented throughout the learning process and serves to continuously confirm student comprehension. This ongoing evaluation provides essential opportunities for necessary corrections, clarifications, and enrichment activities, enabling responsive instructional adjustments. Formative assessment data informs real-time decision-making by educators, supporting differentiated instruction and individualized learning pathways.
Conversely, summative assessment, aligned with design validation, provides a comprehensive evaluation of the entire learning period, ultimately verifying whether learners have attained the established learning objectives and acquired the competencies required for their educational or professional advancement. While formative assessment emphasizes continuous improvement during the learning journey, summative assessment determines the final outcome and readiness for next steps.
The relationship between these two assessment types is not competitive but rather synergistic. Formative assessment throughout a course creates a foundation of evidence supporting summative assessment outcomes. When formative assessments are well-designed and systematically analyzed, they enhance the validity and reliability of subsequent summative evaluations. Conversely, summative assessment results can inform educators about the overall effectiveness of formative assessment strategies and the curriculum itself, contributing to continuous educational improvement.
Contemporary Educational Context and Assessment Integration
Modern educational frameworks, reflected in curriculum standards and educational guidelines across many jurisdictions, increasingly emphasize the importance of balanced assessment systems that integrate both formative and summative approaches. Contemporary educational philosophy recognizes that effective learning involves not only the acquisition of factual knowledge but also the development of critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and professional attitudes and dispositions. This expanded understanding of learning outcomes necessitates sophisticated assessment systems capable of measuring diverse competencies.
Educational reform initiatives worldwide are placing greater emphasis on assessment literacy among educators, advocating for the strategic use of both formative and summative methods to provide comprehensive insights into student learning. The integration of formative assessment data collection and analysis into routine instructional practice has become increasingly emphasized in evidence-based teaching methodologies. Educators are encouraged to employ multiple formative assessment techniques to gather diverse evidence of student understanding, thereby creating a more nuanced and complete picture of learner progress.
Furthermore, technological advances in educational assessment have expanded the capacity for continuous, embedded formative assessment through learning management systems, educational data analytics, and adaptive learning platforms. These tools enable more frequent and detailed monitoring of student progress while reducing assessment burden compared to traditional paper-based approaches.
Practical Implementation: Best Practices for Educators
To maximize the effectiveness of both formative and summative assessment, educators should consider the following practices: establish clear learning objectives aligned with both assessment types; employ a variety of formative assessment techniques suited to different learning contexts and learner needs; provide timely, constructive feedback from formative assessments that guides student improvement; maintain assessment records documenting student progress over time; use formative assessment data to make instructional adjustments; design summative assessments that validly and reliably measure achievement of stated learning objectives; and reflect on assessment data to evaluate the effectiveness of instruction and identify areas for curriculum improvement.
Conclusion
The essential distinction between formative and summative assessment lies in their timing, purpose, and application within the educational process. Formative assessment serves as an ongoing diagnostic and instructional tool, providing continuous feedback to support learning improvement during the course of instruction. Summative assessment provides definitive evaluation of overall achievement at the conclusion of a learning period. Both assessment methods are integral to effective educational practice and warrant deep conceptual understanding and skillful implementation by educational professionals. The thoughtful integration of formative and summative assessment creates a comprehensive evaluation system that supports student learning, informs instructional decision-making, and provides evidence of educational effectiveness. In contemporary educational contexts, where diverse competencies and higher-order thinking skills are increasingly valued, the strategic and balanced use of both formative and summative assessment approaches is essential to developing learners prepared for academic success and professional contribution.
Related Articles
- Understanding the Difference Between Validation and Verification
- Understanding the Differences Between Correction, Corrective Action, and Preventive Action
- Understanding the Difference Between Computerized Systems and Computer Systems
- Understanding the Differences Between FDA Form 483 and Warning Letters: Issuance Processes and Corporate Impact
- Understanding the Difference Between “Design” and “Design Control” in Medical Devices
- Understanding the Difference Between Risks and Issues

Comment