History of FDA Medical Device Regulation
On July 21, 1978, FDA issued a final rule in the Federal Register (43 FR 31508) establishing cGMP requirements for medical devices under section 520(f) of the FD&C Act (medical device GMP).
Such regulations became effective on December 18, 1978 and were codified under Part 820.
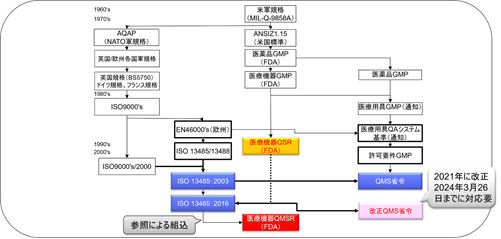
Medical Device GMPChanged to QSRGMP changed to QSR.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practice, a code of practice.
In the case of pharmaceuticals, most recall cases are due to manufacturing quality. In the case of medical devices, however, even if they are manufactured properly according to the drawings, if the design was wrong in the first place, they will not be safe medical devices.
In other words, proper design control is necessary to ensure the safety of medical devices.
Safety of Medical Devices Act (SMDA)
Published on July 21, 1978, the GMP Regulations set requirements for the manufacturing and quality control of medical devices, which remained largely unchanged until 1990, when the Safe Medical Device Act (SMDA) was passed.
The SMDA is a change in the law based on the finding that a significant percentage of equipment recalls are due to defects in product design.
The SMDA called for the inclusion of Design Control requirements in GMP regulations and efforts toward GMP mutual recognition agreements with foreign countries.
The SMDA gave the FDA the authority to add design controls to the cGMP regulations. The FDA amended the GMP regulations under the SMDA to add the new design control provisions, and at the same time, the FDA adopted a policy of aligning the GMP regulations as closely as possible with the quality system requirements contained in the international standard (ISO 9001).
From Medical Device GMP to QSR
The movement to revise GMP regulations began with the Medical Device GMP Advisory Committee meeting in April 1990.
From that year through 1995, various steps were taken toward rule revision, including Advance Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, publication of proposed rules for public comment, use of GMP Working Drafts and public notice requesting comments on the drafts, holding GMP public hearings, and holding GMP Advisory Committee meetings. The FDA’s decision to revise medical device GMP was based on the progress of various steps toward rule revision, including the convening of the GMP Advisory Committee, as well as the analysis of device recall data and the evaluation of international quality standards.
To implement the changes made by the SMDA, the FDA revised Part 820 in 1996 and established the current Quality System Regulation (QSR).
It was determined that it would be more reasonable to establish a broad framework that all manufacturers must follow rather than to prescribe detailed manufacturing requirements for specific devices because the medical device GMP regulations must apply to many different types of medical devices.
To that end, FDA promulgated a new rule called the “Quality System” (QS) on October 7, 1996, as a final GMP rule with changes to the proposed rule and work group drafts to give manufacturers more flexibility in meeting quality requirements.
The QSR was created on the basis of ISO 13485:1996/ISO 9001:1994.
QSRs include procedures used in the design, purchase, manufacture, packaging, labeling, storage, installation, and servicing of medical devices, as well as requirements for equipment and controls used for these procedures.
Since the time of the QSR’s enactment, the FDA has sought to harmonize cGMP regulations as much as possible with the quality management system requirements contained in the international standards applicable at that time.
FDA worked closely with GHTF and ISO Technical Committee 210 (TC 210).
QSRs include procedures used in the design, purchase, manufacture, packaging, labeling, storage, installation, and servicing of medical devices, as well as requirements for equipment and controls used for these procedures.
The regulation defines Quality as the totality of features and characteristics that support the ability of equipment to meet its fitness-for-use requirements, including safety and performance, and Quality System (QS) as the organizational structure, responsibilities, procedures, processes, and resources for the implementation of quality management.
From QSR to QMSR
On February 23, 2022, the FDA published an amendment to harmonize the QSR with ISO 13485:2016.
The QMSR will align many of its requirements with ISO 13485:2016 by incorporating the requirements of ISO 13485:2016.
On the other hand, it adds additional requirements to ISO 13485:2016 regarding the retention of complaint files and other records.
The FDA currently plans to finalize the QMSR by approximately December 2023. The transitional period appears to be undecided due to various opinions.


Comment